Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
前川 禎通; 吉川 貴史*; 中堂 博之; 家田 淳一; 齊藤 英治
Journal of Applied Physics, 133(2), p.020902_1 - 020902_24, 2023/01
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:96.84(Physics, Applied)Along with the progress of spin science and spintronics research, the flow of electron spins, i.e., spin current, has attracted interest. New phenomena and electronic states were explained in succession using the concept of spin current. Moreover, as many of the conventionally known spintronics phenomena became well organized based on spin current, it has rapidly been recognized as an essential concept in a wide range of condensed matter physics. In this article, we focus on recent developments in the physics of spin, spin current, and their related phenomena, where the conversion between spin angular momentum and different forms of angular momentum plays an essential role. Starting with an introduction to spin current, we first discuss the recent progress in spintronic phenomena driven by spin-exchange coupling: spin pumping, topological Hall torque, and emergent inductor. We, then, extend our discussion to the interaction/interconversion of spins with heat, lattice vibrations, and charge current and address recent progress and perspectives on the spin Seebeck and Peltier effects. Next, we review the interaction between mechanical motion and electron/nuclear spins and argue the difference between the Barnett field and rotational Doppler effect. We show that the Barnett effect reveals the angular momentum compensation temperature, at which the net angular momentum is quenched in ferrimagnets.
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures
/Pt heterostructures家田 淳一; 岡安 悟; 針井 一哉*; 小畠 雅明; 吉井 賢資; 福田 竜生; 石田 真彦*; 齊藤 英治
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1301106_1 - 1301106_6, 2022/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:22.45(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)スピンゼーベック効果(SSE)に基づくスピン駆動熱電(STE)デバイスと、熱源としての放射性同位元素の組み合わせは、宇宙探査機の電源などの応用における次世代の発電方法としての可能性を秘めている。しかし、スピン熱電デバイスの照射耐性を示す利用可能な知識は非常に限られている。重イオンビーム加速器と硬X線光電子分光法(HAXPES)測定を使用した分析を通じて、Y Fe
Fe O
O /Ptヘテロ構造に基づく典型的なSTEデバイスが高エネルギー重イオンビームの照射に対する耐性を持つことを検証する。使用済み核燃料の表面から放出される核分裂生成物による累積損傷をモデル化した320MeVの金イオンビームを使用し、線量レベルを変えることにより、SSE要素の熱電および磁気特性が
/Ptヘテロ構造に基づく典型的なSTEデバイスが高エネルギー重イオンビームの照射に対する耐性を持つことを検証する。使用済み核燃料の表面から放出される核分裂生成物による累積損傷をモデル化した320MeVの金イオンビームを使用し、線量レベルを変えることにより、SSE要素の熱電および磁気特性が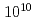 イオン/cm
イオン/cm フルエンスまでのイオン照射線量の影響を受けず、イオントラックがサンプル表面をほぼ完全に覆う約
フルエンスまでのイオン照射線量の影響を受けず、イオントラックがサンプル表面をほぼ完全に覆う約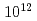 イオン/cm
イオン/cm でSSE信号が消滅することを確認した。さらに、HAXPES測定は、Y
でSSE信号が消滅することを確認した。さらに、HAXPES測定は、Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt界面への影響を理解するために実行した。HAXPES測定は、SSE信号を減少させる化学反応が照射線量の増加とともに強化されることを示唆している。過酷な環境使用に適用できるより優れたSTEデバイスを開発するために、Y
/Pt界面への影響を理解するために実行した。HAXPES測定は、SSE信号を減少させる化学反応が照射線量の増加とともに強化されることを示唆している。過酷な環境使用に適用できるより優れたSTEデバイスを開発するために、Y Fe
Fe O
O /Ptで損傷分析の現在の理解を共有したい。
/Ptで損傷分析の現在の理解を共有したい。
Chen, Y.*; 佐藤 正寛*; Tang, Y.*; 塩見 雄毅*; 大柳 洸一*; 益田 隆嗣*; 南部 雄亮*; 藤田 全基*; 齊藤 英治
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.5199_1 - 5199_7, 2021/08
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:61.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A triplon refers to a fictitious particle that carries angular momentum 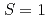 corresponding to the elementary excitation in a broad class of quantum dimerized spin systems. Such systems without magnetic order have long been studied as a testing ground for quantum properties of spins. Although triplons have been found to play a central role in thermal and magnetic properties in dimerized magnets with singlet correlation, a spin angular momentum flow carried by triplons, a triplon current, has not been detected yet. Here we report spin Seebeck effects induced by a triplon current: triplon spin Seebeck effect, using a spin-Peierls system CuGeO
corresponding to the elementary excitation in a broad class of quantum dimerized spin systems. Such systems without magnetic order have long been studied as a testing ground for quantum properties of spins. Although triplons have been found to play a central role in thermal and magnetic properties in dimerized magnets with singlet correlation, a spin angular momentum flow carried by triplons, a triplon current, has not been detected yet. Here we report spin Seebeck effects induced by a triplon current: triplon spin Seebeck effect, using a spin-Peierls system CuGeO . The result shows that the heating-driven triplon transport induces spin current whose sign is positive, opposite to the spin-wave cases in magnets. The triplon spin Seebeck effect persists far below the spin-Peierls transition temperature, being consistent with a theoretical calculation for triplon spin Seebeck effects.
. The result shows that the heating-driven triplon transport induces spin current whose sign is positive, opposite to the spin-wave cases in magnets. The triplon spin Seebeck effect persists far below the spin-Peierls transition temperature, being consistent with a theoretical calculation for triplon spin Seebeck effects.
吉川 貴史*; Reitz, D.*; 伊藤 宏陽*; 巻内 崇彦*; 杉本 宜陽*; 恒川 翔*; 大門 俊介*; 大柳 洸一*; Ramos, R.*; 高橋 三郎*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.4356_1 - 4356_7, 2021/07
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:88.38(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Thermoelectric effects have been applied to power generators and temperature sensors that convert waste heat into electricity. The effects, however, have been limited to electrons to occur, and inevitably disappear at low temperatures due to electronic entropy quenching. Here, we report thermoelectric generation caused by nuclear spins in a solid: nuclear-spin Seebeck effect. The sample is a magnetically ordered material MnCO having a large nuclear spin
having a large nuclear spin 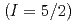 of
of  Mn nuclei and strong hyperfine coupling, with a Pt contact. In the system, we observe low-temperature thermoelectric signals down to 100 mK due to nuclear-spin excitation. Our theoretical calculation in which interfacial Korringa process is taken into consideration quantitatively reproduces the results. The nuclear thermoelectric effect demonstrated here offers a way for exploring thermoelectric science and technologies at ultralow temperatures.
Mn nuclei and strong hyperfine coupling, with a Pt contact. In the system, we observe low-temperature thermoelectric signals down to 100 mK due to nuclear-spin excitation. Our theoretical calculation in which interfacial Korringa process is taken into consideration quantitatively reproduces the results. The nuclear thermoelectric effect demonstrated here offers a way for exploring thermoelectric science and technologies at ultralow temperatures.
Frost, W.*; 関 剛斎*; 窪田 崇秀*; Ramos, R.*; 齊藤 英治; 高梨 弘毅*; 廣畑 貴文*
Applied Physics Letters, 118(17), p.172405_1 - 172405_5, 2021/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:7.86(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate that the spin-Seebeck effect can be used to estimate the volume of edge domains formed in a giant magnetoresistive (GMR) device. The thermal gradient induced by Joule heating can be harnessed by the addition of a ferromagnetically insulating channel of Fe O
O on the sides of the GMR pillar. This generates a spin wave in Fe
on the sides of the GMR pillar. This generates a spin wave in Fe O
O , which couples with the free-layer edge magnetization and controls the reversal of the ferromagnetic layers in one direction only, increasing the current density from
, which couples with the free-layer edge magnetization and controls the reversal of the ferromagnetic layers in one direction only, increasing the current density from 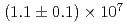 A/cm
A/cm to
to 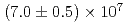 A/cm
A/cm . By simple assumption, we estimate the effect of the edge domain on magnetization reversal to be
. By simple assumption, we estimate the effect of the edge domain on magnetization reversal to be 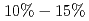 by spin-transfer torque.
by spin-transfer torque.
岡安 悟; 針井 一哉*; 小畠 雅明; 吉井 賢資; 福田 竜生; 石田 真彦*; 家田 淳一; 齊藤 英治
Journal of Applied Physics, 128(8), p.083902_1 - 083902_7, 2020/08
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:19.49(Physics, Applied)The ion-irradiation tolerance of thermoelectric devices based on the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) was investigated by using 320 MeV gold ion (Au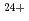 ) beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. For this purpose, prototypical Pt/Y
) beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. For this purpose, prototypical Pt/Y Fe
Fe O
O /Gd
/Gd Ga
Ga O
O SSE elements were irradiated with varying the dose level at room temperature and measured the SSE voltage of them. We confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation up to
SSE elements were irradiated with varying the dose level at room temperature and measured the SSE voltage of them. We confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation up to 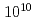 ions/cm
ions/cm fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around
fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around 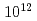 ions/cm
ions/cm , in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. We also performed the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements to understand the effects at the interface of Pt/Y
, in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. We also performed the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements to understand the effects at the interface of Pt/Y Fe
Fe O
O . The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. The present study demonstrates that SSE-based devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in harsh environments for a long time period.
. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. The present study demonstrates that SSE-based devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in harsh environments for a long time period.
大柳 洸一*; 吉川 貴史*; 齊藤 英治
AIP Advances (Internet), 10(1), p.015031_1 - 015031_5, 2020/01
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:71.02(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We report the nonlocal spin Seebeck effect (nlSSE) in a lateral configuration of Pt/Y Fe
Fe O
O (YIG)/Pt systems as a function of the magnetic field
(YIG)/Pt systems as a function of the magnetic field  (up to 10 T) at various temperatures
(up to 10 T) at various temperatures  (3 K
(3 K  300 K). The nlSSE voltage decreases with increasing B in a linear regime with respect to the input power (the applied charge-current squared
300 K). The nlSSE voltage decreases with increasing B in a linear regime with respect to the input power (the applied charge-current squared 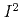 ). The reduction of the nlSSE becomes substantial when the Zeeman energy exceeds thermal energy at low temperatures, which can be interpreted as freeze-out of magnons relevant for the nlSSE. Furthermore, we found the nonlinear power dependence of the nlSSE with increasing
). The reduction of the nlSSE becomes substantial when the Zeeman energy exceeds thermal energy at low temperatures, which can be interpreted as freeze-out of magnons relevant for the nlSSE. Furthermore, we found the nonlinear power dependence of the nlSSE with increasing  at low temperatures (
at low temperatures (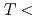 20 K), at which the B-induced signal reduction became less visible. Our experimental results suggest that in the nonlinear regime, high-energy magnons are overpopulated compared to those expected from the thermal energy. We also estimate the magnon spin diffusion length as functions of
20 K), at which the B-induced signal reduction became less visible. Our experimental results suggest that in the nonlinear regime, high-energy magnons are overpopulated compared to those expected from the thermal energy. We also estimate the magnon spin diffusion length as functions of  and
and  .
.
八尋 黎明*; 吉川 貴史*; Ramos, R.*; 大柳 洸一*; 日置 友智*; 大門 俊介*; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review B, 101(2), p.024407_1 - 024407_7, 2020/01
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:77.9(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report the observation of anomalous peak structures induced by hybridized magnon-phonon excitation (magnon polarons) in the magnetic field dependence of the spin Peltier effect (SPE) in a Lu Bi
Bi Fe
Fe Ga
Ga O
O (BiGa:LuIG) with Pt contact. The SPE peaks coincide with magnetic fields tuned to the threshold of magnonpolaron formation, consistent with the previous observation in the spin Seebeck effect. The enhancement of SPE is attributed to the lifetime increase in spin current caused by magnon-phonon hybridization in BiGa:LuIG.
(BiGa:LuIG) with Pt contact. The SPE peaks coincide with magnetic fields tuned to the threshold of magnonpolaron formation, consistent with the previous observation in the spin Seebeck effect. The enhancement of SPE is attributed to the lifetime increase in spin current caused by magnon-phonon hybridization in BiGa:LuIG.
Ramos, R.*; 日置 友智*; 橋本 佑介*; 吉川 貴史*; Frey, P.*; Kreil, A. J. E.*; Vasyuchka, V. I.*; Serga, A. A.*; Hillebrands, B.*; 齊藤 英治
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.5162_1 - 5162_8, 2019/11
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:76.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Resonant enhancement of spin Seebeck effect (SSE) due to phonons was recently discovered in Y Fe
Fe O
O (YIG). This effect is explained by hybridization between the magnon and phonon dispersions. However, this effect was observed at low temperatures and high magnetic fields, limiting the scope for applications. Here we report observation of phonon-resonant enhancement of SSE at room temperature and low magnetic field. We observe in Lu
(YIG). This effect is explained by hybridization between the magnon and phonon dispersions. However, this effect was observed at low temperatures and high magnetic fields, limiting the scope for applications. Here we report observation of phonon-resonant enhancement of SSE at room temperature and low magnetic field. We observe in Lu BiFe
BiFe GaO
GaO an enhancement 700% greater than that in a YIG film and at very low magnetic fields around 10
an enhancement 700% greater than that in a YIG film and at very low magnetic fields around 10 T, almost one order of magnitude lower than that of YIG. The result can be explained by the change in the magnon dispersion induced by magnetic compensation due to the presence of non-magnetic ion substitutions. Our study provides a way to tune the magnon response in a crystal by chemical doping, with potential applications for spintronic devices.
T, almost one order of magnitude lower than that of YIG. The result can be explained by the change in the magnon dispersion induced by magnetic compensation due to the presence of non-magnetic ion substitutions. Our study provides a way to tune the magnon response in a crystal by chemical doping, with potential applications for spintronic devices.
廣部 大地*; 佐藤 正寛*; 萩原 雅人*; 塩見 雄毅*; 益田 隆嗣*; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review Letters, 123(11), p.117202_1 - 117202_7, 2019/09
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:65.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Investigating exotic magnetic materials with spintronic techniques is effective at advancing magnetism as well as spintronics. In this work, we report unusual field-induced suppression of the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) in a quasi-one-dimensional frustrated spin- magnet LiCuVO
magnet LiCuVO , known to exhibit spin-nematic correlation in a wide range of external magnetic field
, known to exhibit spin-nematic correlation in a wide range of external magnetic field  . The suppression takes place above
. The suppression takes place above 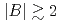 T in spite of the
T in spite of the  -linear isothermal magnetization curves in the same
-linear isothermal magnetization curves in the same  range. The result can be attributed to the growth of the spin-nematic correlation while increasing
range. The result can be attributed to the growth of the spin-nematic correlation while increasing  . The correlation stabilizes magnon pairs carrying spin 2, thereby suppressing the interfacial spin injection of SSE by preventing the spin-1 exchange between single magnons and conduction electrons at the interface. This interpretation is supported by integrating thermodynamic measurements and theoretical analysis on the SSE.
. The correlation stabilizes magnon pairs carrying spin 2, thereby suppressing the interfacial spin injection of SSE by preventing the spin-1 exchange between single magnons and conduction electrons at the interface. This interpretation is supported by integrating thermodynamic measurements and theoretical analysis on the SSE.
 and CrGeTe
and CrGeTe
伊東 直洋*; 吉川 貴史*; Barker, J.*; 廣部 大地*; 塩見 雄毅*; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review B, 100(6), p.060402_1 - 060402_6, 2019/08
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:88.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the longitudinal spin Seebeck effect (LSSE) in the layered ferromagnetic insulators CrSiTe and CrGeTe
and CrGeTe covered by Pt films in the measurement configuration where spin current traverses the ferromagnetic Cr layers. The LSSE response is clearly observed in the ferromagnetic phase and, in contrast to a standard LSSE magnet Y
covered by Pt films in the measurement configuration where spin current traverses the ferromagnetic Cr layers. The LSSE response is clearly observed in the ferromagnetic phase and, in contrast to a standard LSSE magnet Y Fe
Fe O
O , persists above the critical temperatures in both CrSiTe
, persists above the critical temperatures in both CrSiTe /Pt and CrGeTe
/Pt and CrGeTe /Pt samples. With the help of a numerical calculation, we attribute the LSSE signals observed in the paramagnetic regime to exchange-dominated interlayer transport of in-plane paramagnetic moments reinforced by short-range ferromagnetic correlations and strong Zeeman effects.
/Pt samples. With the help of a numerical calculation, we attribute the LSSE signals observed in the paramagnetic regime to exchange-dominated interlayer transport of in-plane paramagnetic moments reinforced by short-range ferromagnetic correlations and strong Zeeman effects.
大沼 悠一; 松尾 衛*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
まぐね, 12(5), p.217 - 224, 2017/10
熱とスピンの相互変換現象であるスピンゼーベック効果及びスピンペルチェ効果について微視的理論に基づき議論を行う。まずはじめに、熱流からスピン流を生成するスピンゼーベック効果について議論する。スピンゼーベック効果の最近の進展を紹介し、フェリ磁性体でのスピンゼーベック効果の符号反転について説明する。次に、スピン流による熱流生成法であるスピンペルチェ効果について議論する。最後に、スピンゼーベック効果とスピンペルチェ効果がオンサーガの相反関係によってまとめられることを示し、スピンと熱の輸送に関するケルビンの関係式を導出する。
小畠 雅明; 吉井 賢資; 福田 竜生; 川崎 郁斗; 岡根 哲夫; 針井 一哉; 家田 淳一; 日置 友智*; 齊藤 英治
no journal, ,
熱によりスピン流を生み出すスピンゼーベック効果を示すPt/Y Fe
Fe O
O (YIG)系に対し、放射光硬X線光電子分光(HAXPES)により特異物性の起源を明らかにすることを試みた。本系は、外部磁場が存在しない状況でもホール効果を発現する(異常ホール効果)。この起源として、YIG中のFe
(YIG)系に対し、放射光硬X線光電子分光(HAXPES)により特異物性の起源を明らかにすることを試みた。本系は、外部磁場が存在しない状況でもホール効果を発現する(異常ホール効果)。この起源として、YIG中のFe イオンがPt膜に染み出し、磁性を持つ金属間化合物を生成していることが示唆されている。本研究ではHAXPESにより、界面近傍の鉄イオン等の電子状態を測定した。実験はSPring-8の原子力機構ビームラインBL22XUで行った。Fe 1s光電子スペクトルからは、鉄イオンが3+のものと金属的な0価に近い2つの状態が存在することが判明し、このシナリオを支持する結果が得られた。Pt 4fやO 1sスペクトルなども測定しており、詳しい結果は当日報告する。
イオンがPt膜に染み出し、磁性を持つ金属間化合物を生成していることが示唆されている。本研究ではHAXPESにより、界面近傍の鉄イオン等の電子状態を測定した。実験はSPring-8の原子力機構ビームラインBL22XUで行った。Fe 1s光電子スペクトルからは、鉄イオンが3+のものと金属的な0価に近い2つの状態が存在することが判明し、このシナリオを支持する結果が得られた。Pt 4fやO 1sスペクトルなども測定しており、詳しい結果は当日報告する。
岡安 悟; 家田 淳一; 針井 一哉*; 小野 正雄*; 小畠 雅明; 福田 竜生; 吉井 賢資; 石田 真彦*; 齊藤 英治
no journal, ,
放射線に強いとされるスピントロニクス材料の原子力分野での応用を目指し、スピンゼーベック効果(SSE)素子へ高エネルギー重イオン照射を行い、その耐用限度を調べた。その結果、使用済み核燃料間近の過酷な環境下でも十分な性能を維持する見通しを得た。この素材が耐放射線特性に優れたものであれば、同位体電池(原子力電池)への応用や使用済み燃料からの廃熱利用へと利用できる分野が広がると期待できる。
岡安 悟; 針井 一哉; 家田 淳一
not registered
【課題】放射線による劣化が小さく、小型で寿命の長い原子力電池を得る。 【解決手段】この原子力電池1においては、膜厚方向(Z方向)に沿って、基板10の上に強磁性絶縁層20、金属層30が順次形成される。この原子力電池1においては、強磁性絶縁層(強磁性体層)20と金属層30とで熱電変換素子5が構成される。基板10の下側には、放射線を発する線源(熱源)40が接続されている。スピンゼーベック効果による電位差は図中でY軸方向において発生するため、金属層30におけるY軸方向における両端部側にそれぞれ第1電極31、第2電極32が接続される。この原子力電池1における熱電変換素子5(強磁性絶縁層20、金属層30)においては、放射線照射による劣化が発生しにくいため、α線以外の放射線を発する線源40を用いることができる。